Small Molecule-Induced Alterations of Protein Polyubiquitination Revealed by Mass-Spectrometric Ubiquitome Analysis
Führer S, Gallant K, Kaschani F, Kaiser M, Janning P, Waldmann H, Gersch M. (2025) Angew Chem Int Ed Engl.
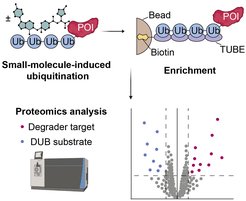
Small molecules which alter protein ubiquitination are emerging as therapeutics due to their ability to modulate targets previously deemed undruggable. These compounds comprise PROTACs, molecular glue degraders and DUB inhibitors, among others. However, methods for the proteome-wide monitoring of compound-induced changes in protein polyubiquitination, which may also detect non-degradative modifications, are lacking. Here, we report the utilization of polyubiquitin enrichment coupled to mass spectrometry to monitor small molecule-induced changes in cellular protein ubiquitination. We established enrichment through tandem ubiquitin binding entities (TUBEs) following semi-denaturing cell lysis and devised an elution protocol compatible with downstream LC-MS/MS analysis. We demonstrate broad applicability of the workflow by assessing ubiquitination changes induced by a PROTAC, a p97 inhibitor and deubiquitinase inhibitors. Application of the assay to compounds inhibiting the deubiquitinase USP7 revealed the induction of non-degradative ubiquitination on the UBE3A E3 ligase. Collectively, we established a versatile proteomics method to facilitate the direct investigation of cellular polyubiquitination, with high relevance for the identification and characterization of protein degraders, stabilizers and other molecules with ubiquitin-mediated bioactivity.