Development of a PDEδ targeting PROTAC that impairs lipid metabolism
Winzker M, Friese A, Koch U, Janning P, Ziegler S. Waldmann H (2019). Angew Chem Int Ed Engl
doi: 10.1002/anie.201913712.
The Waldmann group developed a new proteolysis targeting chimera (PROTAC) which efficiently and selectively reduced PDEδ levels in cells through induced proteasomal degradation.
Its application increased sterol regulatory element binding protein (SREBP)-mediated gene expression of enzymes involved in lipid metabolism, which was accompanied by elevated levels of cholesterol precursors.
This shows that PDEd function plays a role in the regulation of enzymes of the mevalonate pathway.
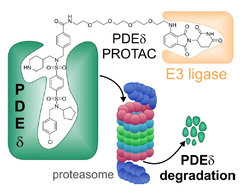
The picomolar PDEd inhibitior Deltasonamide 1 was employed for the design and synthesis of proteolysis-targeting chimera (PROTAC) based on ligands for the E3 ligases cereblon or VHL to target PDEd for degradation. The PROTACs efficiently, selectively and proteasome-dependently deplete PDEd in cells and promise to be valuable tools for chemical PDEd knockdown.
