Stefan Raunser
Director, Structural Biochemistry
News and Press Releases
Research Interests
> Department Structural Biochemistry
Our research concentrates on the molecular understanding of fundamental cellular processes. Firstly, we are interested in membrane homeostasis in eukaryotic cells and secondly we want to understand the molecular details of muscle contraction. Another focus is on the molecular understanding of the mechanism of action of bacterial toxin complexes.
Our overarching goal is to understand the mechanisms underlying these processes in the healthy and diseased organism in molecular detail. To achieve this, it is essential to elucidate the structure and thus the function of the involved proteins and protein complexes.
We perform structural analyses by electron cryomicroscopy (cryo-EM) and electron cryotomography (cryo-ET), fluorescence-based assays and site-directed mutagenesis to determine the structures and functions of these complexes. For their biophysical characterization we employ isothermal titration calorimetry, ESI-MS, bio-layer interferometry, thermophoresis and CD spectroscopy.
The potential of cryo-electron tomography
Zooming in on Muscle Cells
Watch how an international Team led by Prof. Stefan Raunser has produced the first high-resolution 3D image of the sarcomere, the basic contractile unit of skeletal and heart muscle cells, by using electron cryo-tomography (cryo-ET).
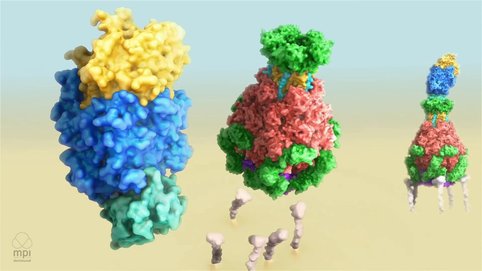
Mechanism of Tc Toxin Action
Selected Publications
Tamborrini D, Wang Z, Wagner T, Tacke S, Stabrin S, Grange M, Kho AL, Rees M, Bennet P, Gautel M, Raunser S (2023). Structure of the native myosin filament in the relaxed cardiac sarcomere. Nature
Source
Rice G, Wagner T, Stabrin M, Sitsel O, Prumbaum D, Raunser S (2023). TomoTwin: generalized 3D localization of macromolecules in cryo-electron tomograms with structural data mining. Nature Methods
Source
Oosterheert W, Klink B. U, Belyy A, Pospich S, Raunser S (2022). Structural Basis of actin filament assembly and aging. Nature
Source
Wang Z, Grange M, Pospich S, Wagner T, Kho A.L, Gautel M, Raunser S (2022). Structures from intact myofibrils reveal mechanism of thin filament regulation through nebulin. Science
Source
Link to freely available Paper!
Wang Z, Grange M, Wagner T, Kho AL, Gautel M, Raunser S (2021). The molecular basis for sarcomere organization in vertebrate skeletal muscle. Cell
Source
Gatsogiannis C, Balogh D, Merino F, Sieber SA, Raunser S (2019). Cryo-EM structure of the ClpXP protein degradation machinery. Nat Struct Mol Bio
Source
Raisch T, Chang CT, Levdansky Y, Muthukumar S, Raunser S, Valkov E (2019). Reconstitution of recombinant human CCR4-NOT reveals molecular insights into regulated deadenylation. Nature Communications
Source
Gatsogiannis C, Merino F, Roderer D, Balchin D, Schubert E, Kuhlee A, Hayer-Hartl M, Raunser S. (2018). Tc toxin activation requires unfolding and refolding of a β-propeller. Nature
Source
Vinayagam D, Mager T, Apelbaum A, Bothe A, Merino F, Hofnagel O, Gatsogiannis C, Raunser S (2018). Electron cryo-microscopy structure of the canonical TRPC4 ion channel. eLife
Source
Klink BU, Zent E, Juneja P, Kuhlee A, Raunser S, Wittinghofer A. (2017). A recombinant BBSome core complex and how it interacts with ciliary cargo. eLife
Source
Pospich S, Kumpula EP, von der Ecken J, Vahokoski J, Kursula I, Raunser S. (2017). Near-atomic structure of jasplakinolide-stabilized malaria parasite F-actin reveals the structural basis of filament instability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
Source
von der Ecken J, Heissler SM, Pathan-Chhatbar S, Manstein DJ & Raunser S (2016).Cryo-EM structure of a human cytoplasmic actomyosin complex at near-atomic resolution. Nature 534(7609):724-28.
Source
freely available!
Gatsogiannis C, Merino F, Serdiuk T, Prumbaum D, Roderer D, Leidreiter F, Meusch D, Müller DJ, and Raunser S (2016). Membrane insertion of a Tc toxin in atomic detail. Nature Structural and Molecular Biology 23(10):884-890.
Source
freely available!
Gatsogiannis C, Hofnagel O, Markl J, Raunser S (2015). Structure of Mega-Hemocyanin reveals protein origami in snails. Structure 23(1):93-103.
Source
Efremov R, Hofnagel O, Raunser S (2015). Architecture and Conformational Switch Mechanism of the Ryanodine Receptor. Nature 517(7532):39-43.
Source
freely available!
Whitney JC, Quentin D, Sawai S, LeRoux M, Harding BN, Ledvina HE, Tran BQ, Robinson H, Goo YA, Goodlett DR, Raunser S, Mougous JD (2015). An Interbacterial NAD(P)(+) Glycohydrolase Toxin Requires Elongation Factor Tu for Delivery to Target Cells. Cell 163(3):607-19.
Source
von der Ecken J, Müller M, Lehman W, Manstein DJ, Penczek PA, Raunser S (2015). Structure of the F-actin-tropomyosin complex. Nature 519(7541):114-7.
Source
freely available!
Meusch D, Gatsogiannis C, Efremov R, Lang A, Hofnagel O, Vetter I, Aktories K, Raunser S (2014). Mechanism of Tc toxin action revealed in molecular detail. Nature 508(7494):61-5.
Source
freely available!
Gatsogiannis C, Lang A, Meusch D, Pfaumann V, Hofnagel O, Benz R, Aktories K, Raunser S (2013). A syringe-like injection mechanism in Photorhabdus luminescens toxins. Nature. 495(7442):520-23
Source
freely available!